What type of breast augmentation incisions are there?
Breast augmentation incisions vary based on the type of breast augmentation (breast implants or fat transfer) and the size and shape of the implant.
There are four common types of breast implant incisions. Your surgeon will select your incision location based on your breast size and shape, implant type, and desired results.
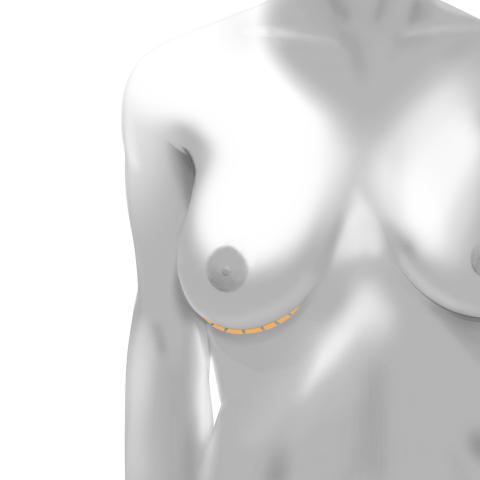
Inframammary Incision
Your surgeon makes an incision underneath your breast, just above the crease. The surgeon then inserts the implant through the incision. If you are getting large implants, your surgeon will likely recommend this approach.
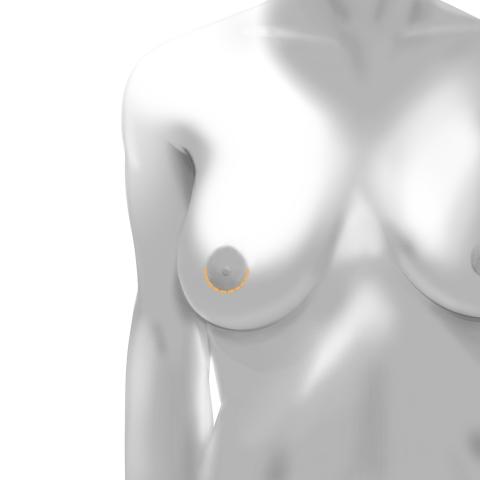
Periareolar Incision
Your surgeon makes an incision around the lower edge of the areola (the dark area surrounding the nipple). The surgeon then inserts the implant through the small incision. This technique is great for smaller implants and produces very little visible scarring. It may have increased risk of capsular contracture compared to the inframammary approach.
Transaxillary Incision
Your surgeon makes an incision near the armpit, where the arm meets the chest area, and inserts the implant. It’s a small incision that is barely noticeable once it heals, but does require more tissue manipulation than other approaches and has additional risks for numbness or changes in muscle function.

Transumbilical Incision
Your surgeon can only use this technique if you’re getting traditional saline implants. This technique is advertised as a ‘scarless’ technique given the incision is in the navel, however it does produce a scar inside the navel and can distort the appearance of a nice belly button. There is also less control over the overall result due to the distance from the breast.
Will I have any scars after my breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation scars vary according to the type of incision your aesthetic surgeon makes (as outlined above).
Although incision lines are permanent, in most cases breast implant scars will fade and significantly improve over time. Aesthetic plastic surgeons make every effort to place incisions in hidden areas and minimize them, with the goal of achieving the desired results with the shortest possible breast augmentation scar. Special tissue handling and suture techniques further reduce scarring.
Your incision healing will depend on the surgical technique, the steps you take to prevent infection (nutrition, not smoking, hydrating), and any underlying medical conditions or genetic tendencies.



